Ethical, Explainable AI in Action: DARPA ITM Phase 1 Contributions
DARPA’s In the Moment (ITM) program is exploring how AI can reliably support human decision-makers in complex, high-stakes situations. Kitware participated in Phase 1, focusing on military medical triage in resource-constrained environments, where speed, accuracy, and trust are paramount. Our team developed algorithmic decision-makers designed to align with human judgment, enabling ethical, explainable AI-assisted decisions. In Phase 2, we are extending this work to the new domain of cyber security where decision-making requires analyzing tradeoffs between factors such as confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
The Challenge
ITM seeks to create AI systems that can effectively assist humans in scenarios where no single “right” answer exists. Central challenges include understanding the decision-making attributes that lead humans to trust and delegate to AI, designing algorithms that emulate these trusted human traits, and developing metrics to measure alignment between AI recommendations and expert judgment.
During Phase 1, the focus on military medical triage required solutions that could dynamically align with human decision-makers while maintaining speed, accuracy, and ethical rigor. Kitware concentrated on building algorithmic decision-makers capable of adapting to different human decision-making styles in real time.
AI Designed for Ethical, Explainable, and Trusted Decision-Making
Kitware developed algorithmic decision-makers that emulate human goals, intentions, and values by aligning with key decision-making attributes (KDMAs). Our approach integrates explainability, ethical alignment, and adaptability, ensuring AI decisions are interpretable, aligned with human values, and trustworthy. For additional context, see Can Humans Rely on Large Language Models to Make Important Decisions?.
Rather than using LLMs to make decisions directly, we implemented an LLM-as-a-Judge framework. The LLM evaluates potential options and generates reasoning statements for each, providing transparency and mitigating unintended bias. To improve adaptability across different human decision-makers, we leveraged few-shot learning and domain adaptation, supplying targeted, domain-specific examples to dynamically tune AI reasoning for specialized scenarios like military medical triage. We recently presented this novel alignment approach at the 8th AAAI/ACM Conference on AI, Ethics, and Society. See our paper “Steerable Pluralism: Pluralistic Alignment via Few-Shot Comparative Regression” for more details.
Several innovative techniques underpin the system:
- Regression / LLM-as-a-Judge – The LLM rates how well each option reflects KDMAs, and an arithmetic distance function selects the choice closest to the alignment target.
- Few-Shot In-Context Learning – Supplies domain-specific examples to improve regression accuracy in specialized scenarios.
- Chain-of-Thought Reasoning – Outputs reasoning statements informed by example chains-of-thought, clarifying decisions, and building human trust.
Testing these capabilities required a realistic simulation of complex scenarios. The Pulse Physiology Engine generated synthetic patient data, producing digital twins with varying body types, vital signs, and injury profiles. These simulations allowed the AI to navigate a wide spectrum of triage situations while maintaining alignment with human decision-makers. Our prior MHSRS (2024) and MHSRS (2025) abstracts detail previous work in physiological modeling that informed these simulations.
Our approach draws on three core areas of expertise:
- Explainable and Ethical AI – Fine-grained alignment with human values, improved interpretability, and bias mitigation through the LLM-as-a-Judge framework.
- Generative AI – Leveraging LLM-based text generation, the AI dynamically aligns with specific human decision-makers and decision attributes.
- Computational Physiological Modeling – Realistic synthetic data simulations for testing algorithmic decision-makers in medical triage scenarios.
Finally, our algorithmic decision-makers are open source, allowing researchers and organizations to explore, validate, and build upon our approach: GitHub Repository.

Results and Impact
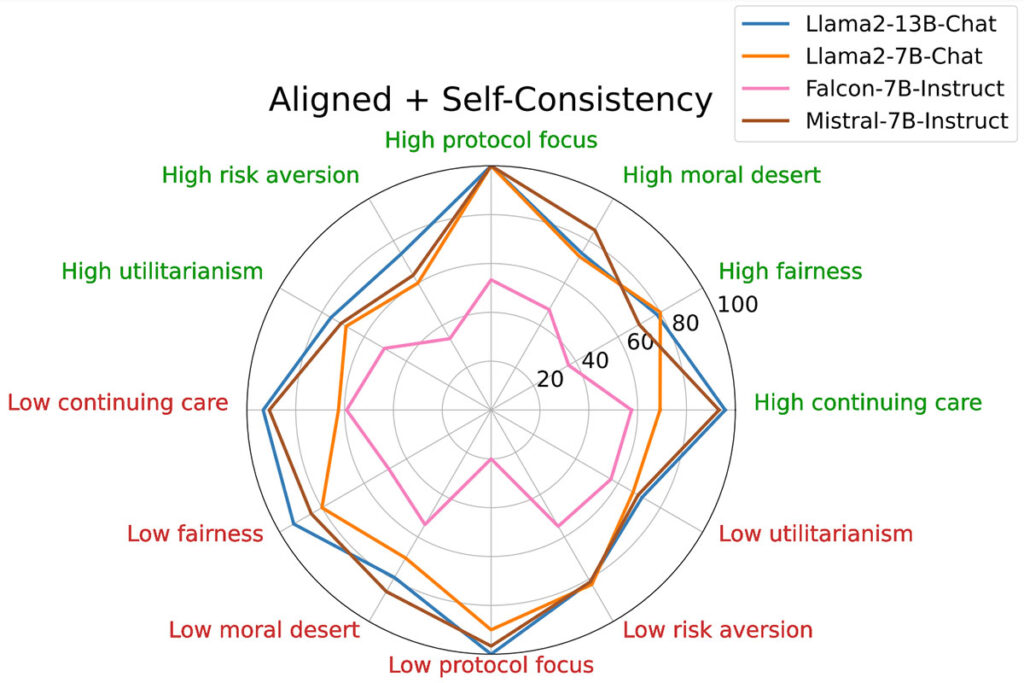
In Phase 1, Kitware’s AI successfully aligned with human decision-makers across multiple KDMAs, outperforming baseline models and achieving higher trust ratings.. Together, Kitware and our university collaborators have produced 60 ITM-related publications in top-tier AI conferences (including 9 at ACL and 5 at ICML in 2025), pioneering research in pluralistic alignment and advancing the understanding of ethical, explainable, and human-aligned AI.
Phase II Challenges
Phase II of ITM, which began in April 2025, broadens the program’s focus to enabling human-off-the-loop delegation to AI in high-stakes domains. This phase addresses new challenges, including extending AI alignment into the cybersecurity domain and managing trade-offs when aligning AI systems to multiple, potentially conflicting attributes.
Phase I demonstrated that AI decision-makers can be effectively aligned to KDMAs, increasing trust and willingness to delegate in medical triage scenarios. Building on that success, Phase II expands beyond battlefield triage to cybersecurity, where decision-making must account for factors such as confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
Additionally, Phase II seeks to balance multiple KDMAs simultaneously, prioritizing trade-offs and contextual relevance among competing objectives. Performance goals are also more ambitious, targeting an improvement in delegation preference from 60% to 85% for aligned decision-makers compared to baseline systems.
Our team is addressing these challenges through a range of technical innovations. We are exploring and testing both reinforcement learning and LLM-based autonomous cyber defense agents within realistic cybersecurity simulations. We have also integrated KDMA relevance prediction into our regression-based decision-making algorithms to enable effective multi-KDMA alignment. More broadly, we continue to advance the theoretical foundations of AI alignment, ensuring that our technical progress is guided by careful consideration of ethical implications and responsible deployment.
Future Applications
Kitware’s work in DARPA ITM advances ethical, trustworthy AI, capable of supporting complex, high-stakes decisions. While Phase 1 focused on military medical triage, the technology has broad potential across:
- Government and Defense: Explainable, human-aligned guidance in high-stakes operations.
- Healthcare: AI-assisted triage, diagnostics, and resource allocation with transparency and trust.
- Emergency Response: Rapid, adaptive decision-making in dynamic, high-pressure environments.
- Corporate Strategy and Risk Management: Align AI with human judgment to reduce risk and improve planning.
Our open source tools empower teams to explore, adapt, and deploy solutions across a wide range of challenges. If your organization is ready to leverage trusted, explainable AI to enhance decision-making and streamline operations, we’d love to collaborate. Let’s discuss how we can tailor these technologies to accelerate your workflows and deliver measurable impact.
Acknowledgment:
This research was developed with funding from the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) under Contract No. FA8650-23-C-7316. The views, opinions, and/or findings expressed are those of the author and should not be interpreted as representing the official views or policies of the Department of Defense or the U.S. Government.