VTK has recently introduced support for ONNX Runtime, opening new opportunities for integrating machine learning inferences into scientific visualization workflows. This feature is also available in ParaView through an official plugin. What are ONNX and ONNX Runtime? ONNX (Open Neural Network eXchange) is an open file format designed to represent machine learning models in a […]


Real-Time Insight with ParaView Catalyst: A Hands-On Guide Part 2: Saving 3D Visualizations
September 30, 2025
High-performance simulations generate massive datasets—but extracting insight from that data shouldn’t be a bottleneck. ParaView Catalyst integrates analysis and visualization directly into the simulation workflow, delivering in situ processing that eliminates the need for slow, storage-heavy post-processing. The result? You get immediate feedback, streamlined workflows, and new opportunities to steer simulations on the fly. Built […]

ParaView 6.0.1 Release Notes
September 29, 2025
Bug fixes made since ParaView 6.0.0 are listed below: Faulty default color map in ParaView 6.0.0 fixed The “Fast” color map, which is the new default in ParaView 6.0.0, was not correctly defined in the ParaView 6.0.0 release. Its color space was set to “Diverging” rather than “Lab”. As a result, the central lightest point […]

The Role of ITK in the Era of Deep Learning in Medical Imaging
September 25, 2025
Deep learning currently dominates the field of medical image analysis. From brain tumor detection to cartilage segmentation and lung nodule analysis, convolutional and transformer-based neural networks often take center stage. Yet, behind every high-performing AI model, there is a need for reliable image preprocessing, spatial normalization, and data handling libraries. This is where the Insight […]
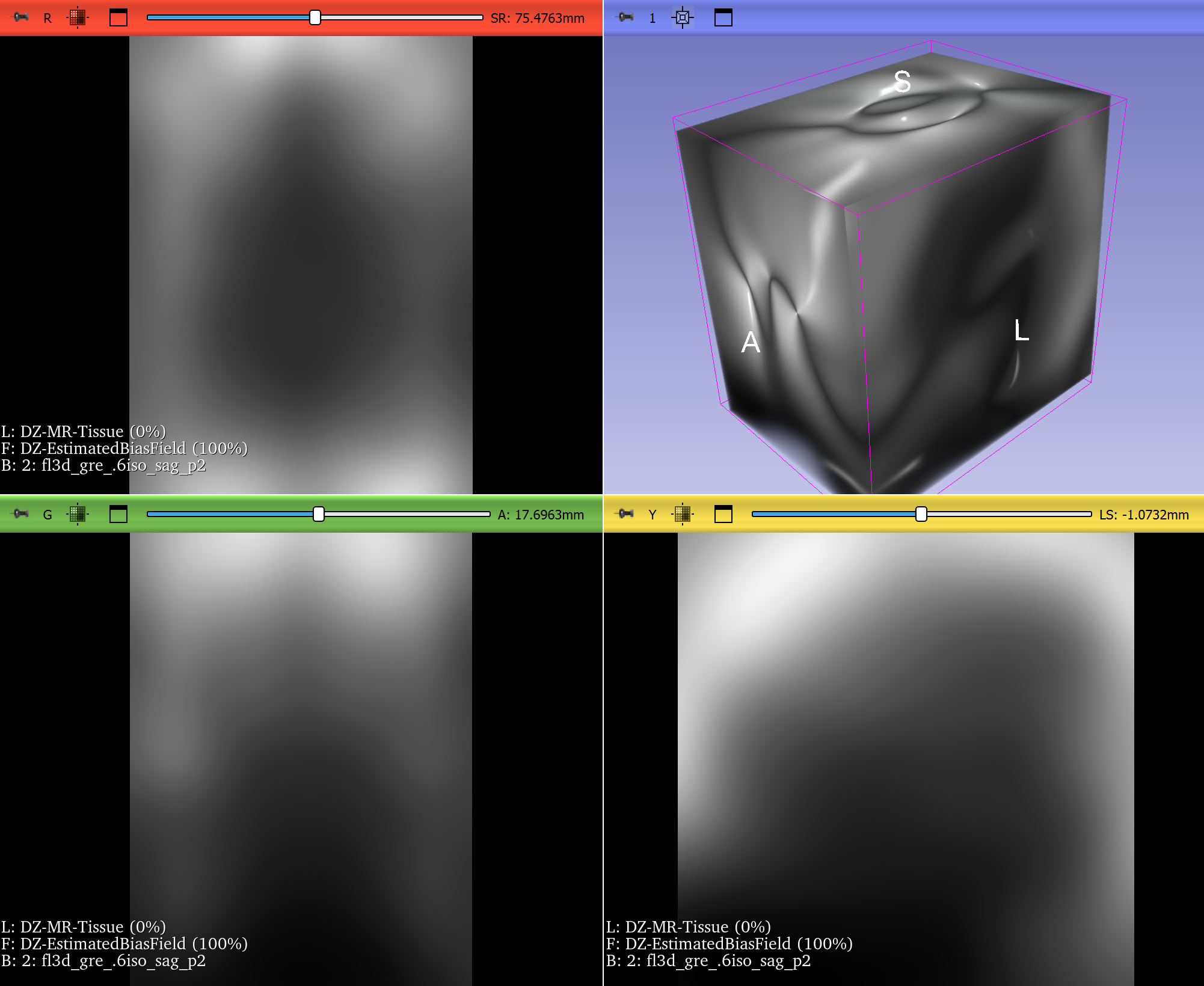
CTest and CDash: Testing without a build system
September 23, 2025
You can send build and test information to CDash even if you aren’t using CMake to build your software. In this blog post, we’ll walk through the steps to set up CTest-driven testing that reports to a CDash dashboard. Following the example of the CMake tutorial where a C++ executable is created to calculate the […]

Using Docker to Simplify the VTK WASM Build Process
September 18, 2025
Are you a C++ developer looking to bring the Visualization Toolkit (VTK) to web applications? As many of you know, transforming a complex C++ library like VTK to compile with WebAssembly (WASM) is a tedious and time-consuming process. The good news is that we’ve made it easier so that you can use pre-built VTK.wasm libraries […]
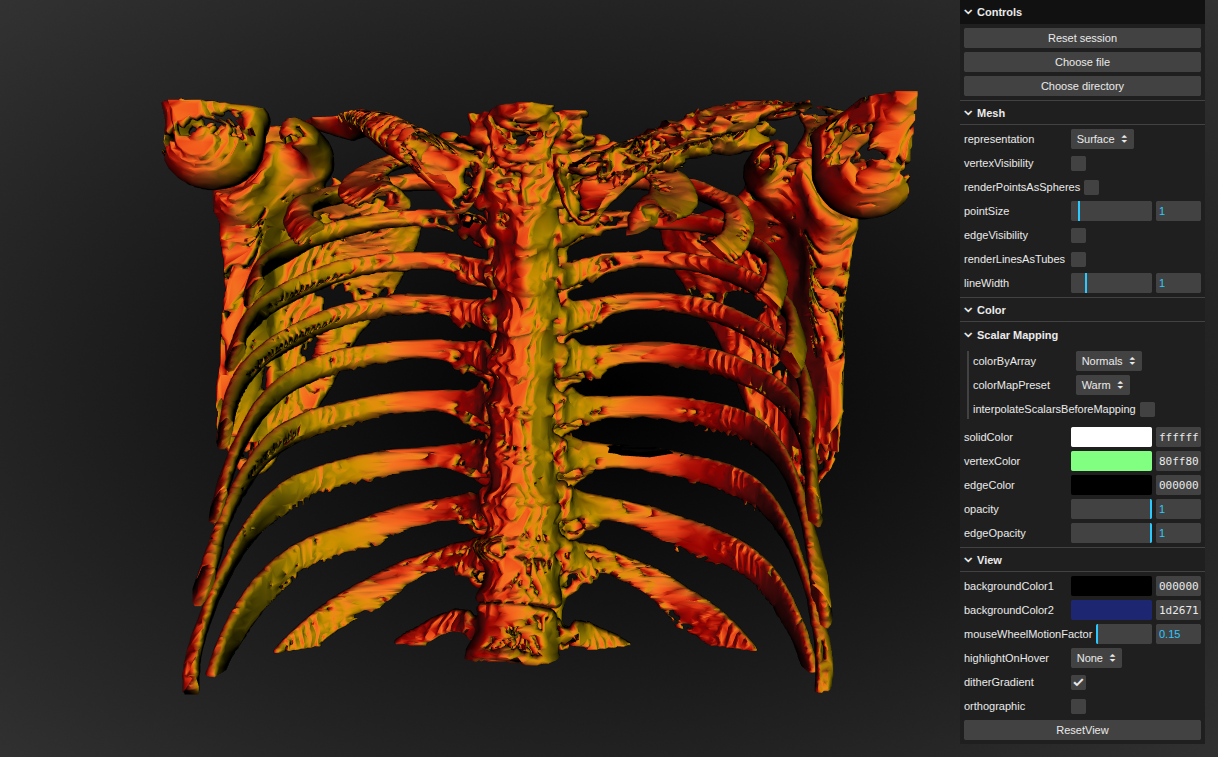
High-performance simulations generate massive datasets—but extracting insight from that data shouldn’t be a bottleneck. ParaView Catalyst integrates analysis and visualization directly into the simulation workflow, delivering in situ processing that eliminates the need for slow, storage-heavy post-processing. The result? You get immediate feedback, streamlined workflows, and new opportunities to steer simulations on the fly. Built […]

Runtime selection between headless, offscreen, and onscreen rendering modes in ParaView
September 3, 2025
This blog documents a major change introduced in ParaView 6.0.0. It also applies to VTK 9.5.0 The ParaView command-line executables pvserver, pvpython and pvbatch now support all three modes of rendering – headless, offscreen, and onscreen in one build. The rendering backend is automatically selected at runtime based upon the system capabilities such as availability of an X server or […]

ParaView Python State File Improvements
August 29, 2025
Python state files in ParaView are a way to create reproducible and editable visualization pipelines. Especially for applications like Catalyst, these state files are intended to be readable, modifiable, and adaptable to different workflows.

OpenLIFU: Accelerating Focused Ultrasound Research with Open Source Hardware and 3D Slicer Driven Software
August 22, 2025
We are excited to showcase a collaboration between Openwater and Kitware Inc. to accelerate the development and adoption of Low-Intensity Focused Ultrasound (LIFU) technology. Combining Openwater’s cutting-edge hardware with Kitware’s expertise in medical software development, we aim to make LIFU accessible to researchers and medical device developers through the OpenLIFU hardware and software suite. Openwater’s […]
Introducing WebAssembly support in VTK
August 15, 2025
Introduction There is increasing demand for powerful, interactive data visualizations directly within web browsers. VTK.wasm is a technology that aims to provide this capability by delivering complex visualization applications without requiring traditional software installations. Not only are these applications portable, but they provide performance at near-native speeds. In this post, we describe some recent steps […]
CppCon 2025
August 15, 2025
CppCon is the premier annual C++ conference, uniting developers from around the world to learn, collaborate, and shape the future of C++. At Kitware, our connection to the C++ community runs deep—our co-founder and Chief Technical Officer, Bill Hoffman, is the original architect of CMake, which has become an essential build system for C++ projects across the globe.

ParaView 6.0 and VTK 9.5: Better Together
August 12, 2025
We are pleased to announce the official releases of ParaView 6.0 and the Visualization Toolkit (VTK) 9.5. This occasion marks a strategic evolution in our release methodology, as we are synchronizing the release schedules of ParaView and VTK for the first time. This alignment is designed to deliver significant advantages to our user and developer […]


How trame Powers Today’s Visualizations
August 4, 2025
Many scientific and engineering applications are still built as standalone desktop tools. While these solutions may have served teams well in the past, they often present modern-day challenges: they’re difficult to share, hard to maintain, and disconnected from today’s collaborative and distributed workflows.
ParaView 6.0.0 Release Notes
August 1, 2025
For a comprehensive list of new features in ParaView 6.0.0, please see the ParaView 6.0.0 release notes hosted on ParaView’s GitLab project page. A selection of notable new features is described on this page. A new default background and color map The default background has changed from “Blue Gray Background” to “Warm Gray Background”. The […]

We previously introduced VolView Insight, a powerful extension of the VolView medical visualization platform, that is designed to integrate imaging studies with real-world clinical data. Built for interoperability and flexibility, Volview Insight allows clinicians and researchers to view medical images, run multimodal AI pipelines, and access relevant patient records, all within a modern and intuitive web […]
